![]()
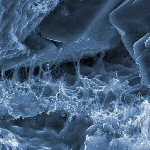
Traditionally pore throat size distribution data is measured using mercury intrusion porosimetry (or MICP). However, this is not always possible /appropriate, so we can also offer pore size distribution data generated from analysis of scanning electron microscope (SEM) images. This methodology is applicable to any lithology (and is well-suited to very fine-grained sediments such as micritic limesonte / chalk). Data can also be collected from fragments of a specific lithology within cuttings samples, extending the “reach” of capillery-pressure type measurements into uncored intervals.
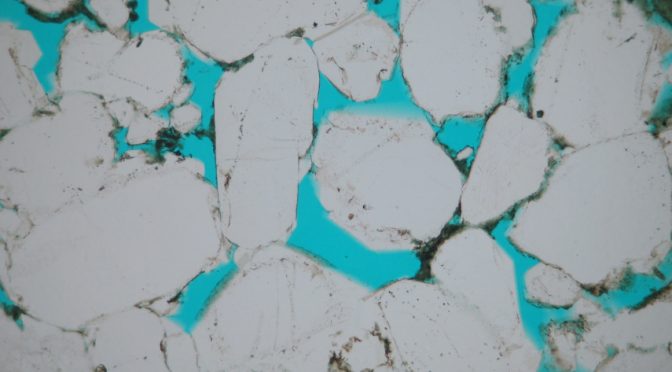
SEM images are collected systematically over an area of, or of random fields within, a polished thin-section. Following segmentation of the images into pores and “grains” (everything else), detailed information on pore volumes and pore sizes is collected.
These results can be used alongside other measures of pore volume and pore size when modelling permeabilities (e.g. helium porosities, mercury intrusion data, and nuclear magnetic resonance data).
Imaging
The strategy for image collection is dependant upon the nature of the sample and its pore system. The SEM magnification is set according to the range in pore size we are attempting to characterise. Depending upon the samples, we may collect images from random, non-contiguous fields over the sample area, or regularly distributed, overlapping fields (that can also be stitched into deep zoom photomontages).
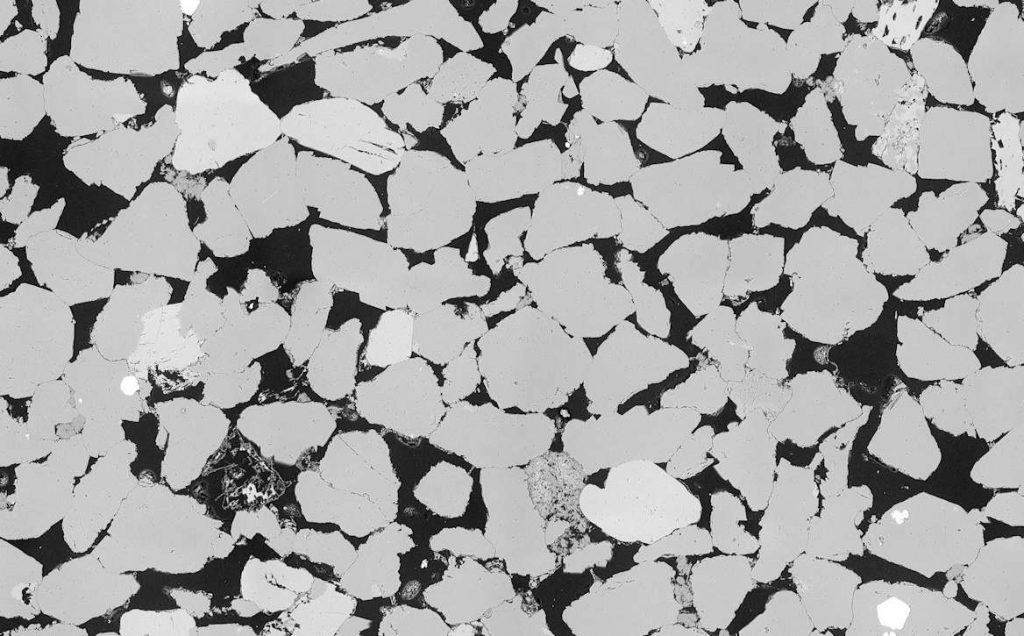

Segmentation
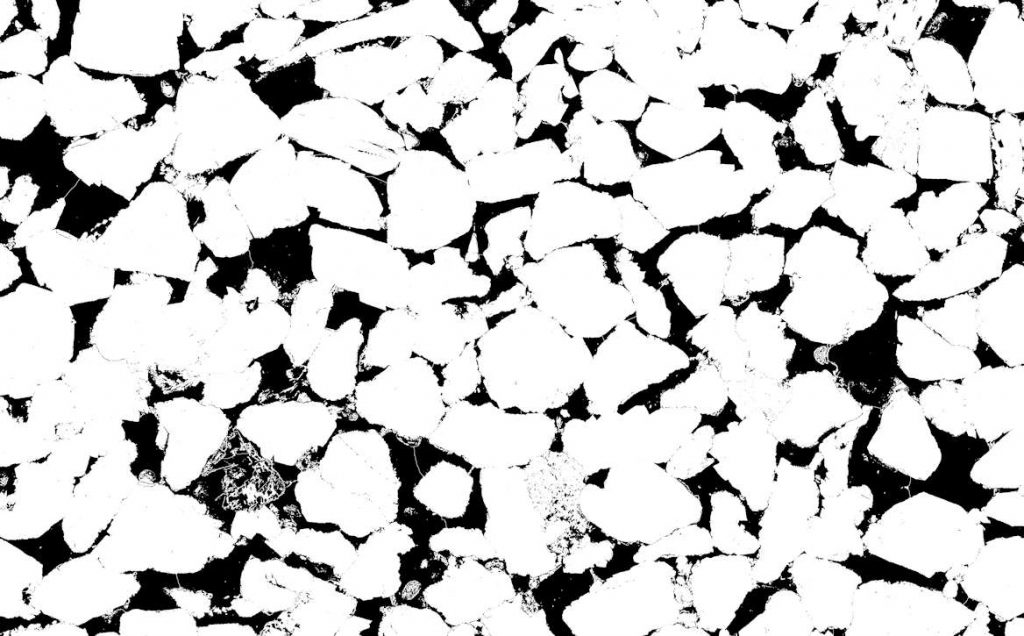

Image analysis routines are used to normalise images to consistent grey-scales and to remove any shading effects. Pores are then segmented from grains and, where required, more advanced routines are used to separate / subdivide touching / connected macropores from one another.
Measurement
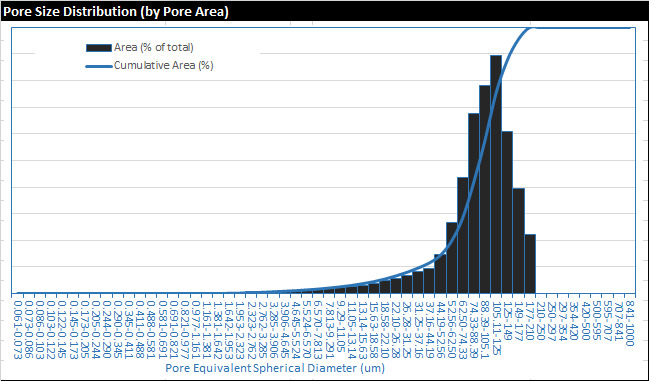
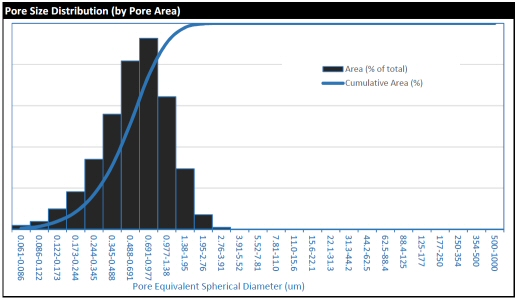
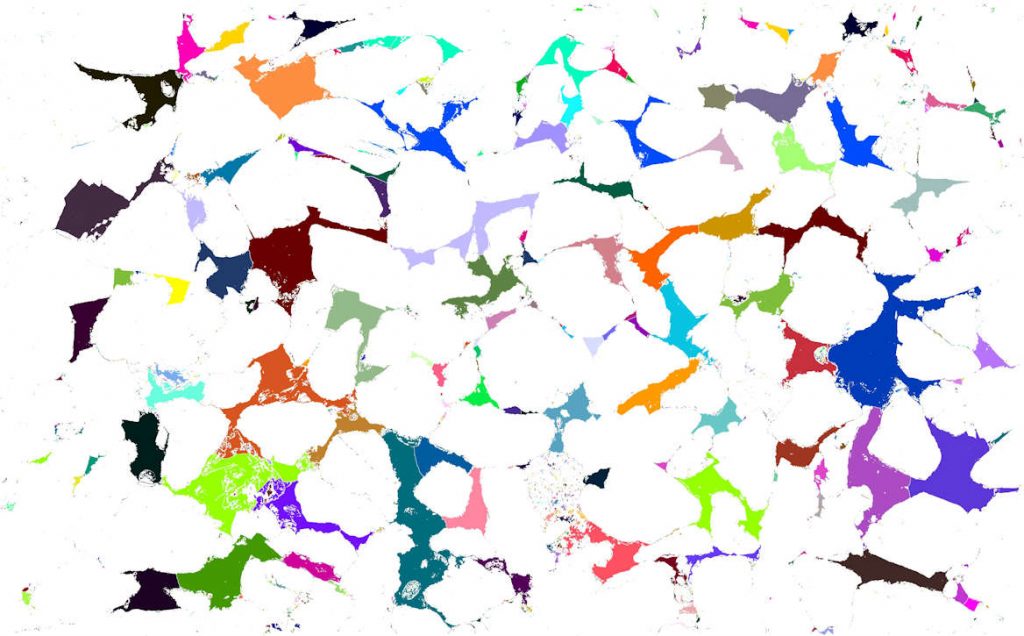
Pore sizes and areas are measured and the results processed to provide total pore areas and pore size distribution data.
Output Data
Results provided include:
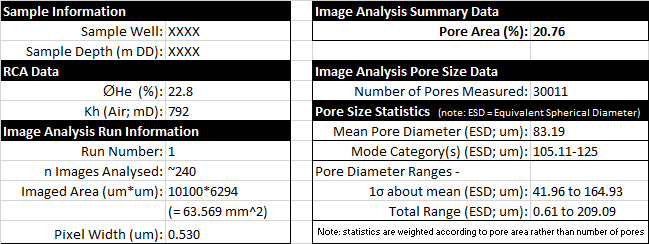
- Summary data (pdf format; including summary and plot shown as below),
- Detailed results (individual pore measurements including pore area, diameter, and other parameters, in xlsx format), and
- either all the original collected images or stitched photomontages (as appropriate, in .tif and/or .jpg format).